Art and technology share a long, intertwined history, evolving together from primitive cave paintings to sophisticated digital creations. This evolution has reshaped not only how art is made, but more importantly, how it is perceived, shared, and monetized. The journey from pigment to pixels reflects humanity’s enduring desire to innovate and express deeper meanings through visual language.
The Origins of Artistic Expression
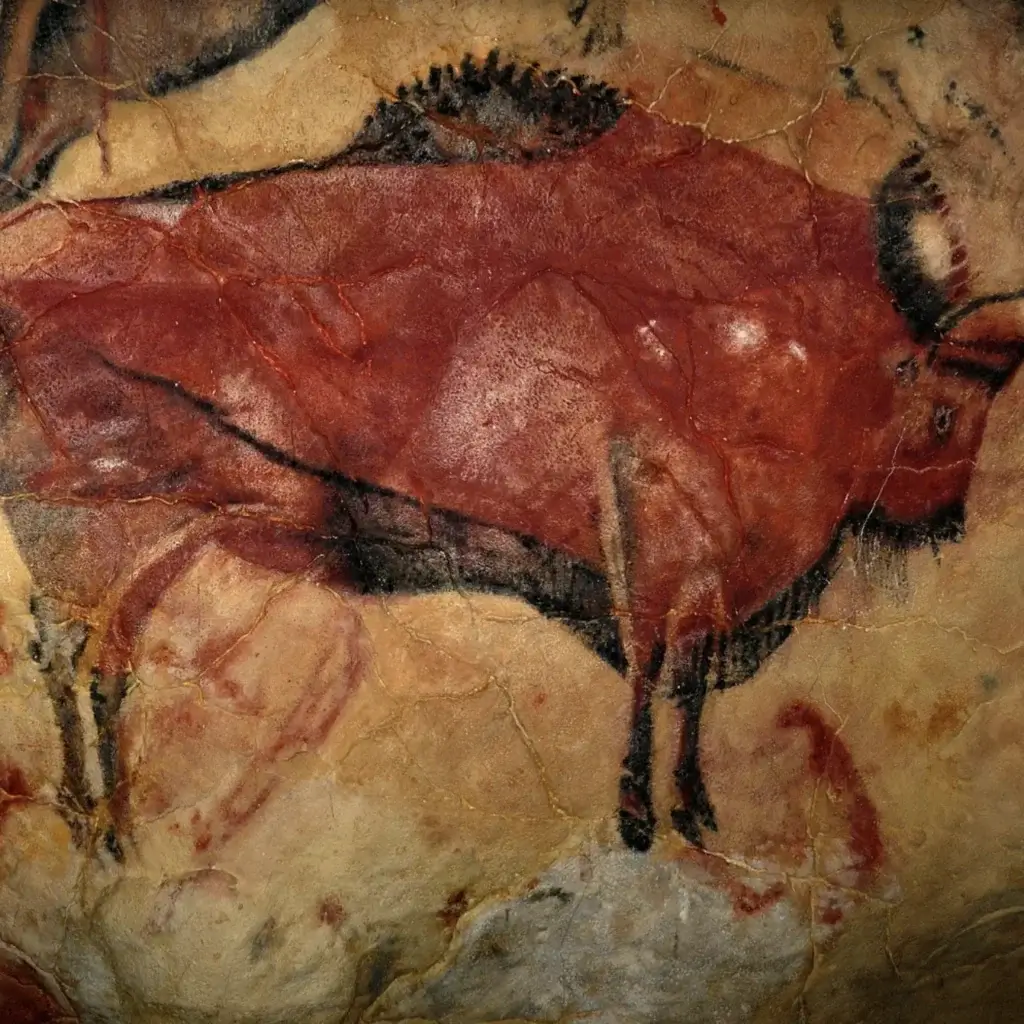
The First Marks: Cave Art and Early Pigments
The story of art begins with our earliest ancestors. Cave paintings discovered in locations like Lascaux and Altamira reveal that art was among humanity’s first forms of communication. These early artists used natural pigments — ochre, charcoal, and hematite — applied with fingers, brushes made of animal hair, or even blown through hollow bones.
The Birth of Tools and Techniques
As human societies advanced, so did their tools. Brushes evolved, surfaces changed from rock to parchment and canvas, and artists developed techniques such as shading, perspective, and layering. These innovations laid the groundwork for the Renaissance and beyond.
Renaissance to Industrial Revolution: Art Meets Mechanics
Renaissance Innovations
The Renaissance marked a turning point in how art was created and understood. With masters like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael, artists blended scientific observation with creative expression. The study of anatomy, light, and proportion brought a new realism and depth to visual art.
The Printing Press and Mass Reproduction
Johannes Gutenberg’s printing press democratized access to art and literature. Reproductions of paintings, engravings, and illustrations could now spread across regions, making art more accessible to the public while also altering artistic commerce.
Mechanization and Photography
The 19th century ushered in the Industrial Revolution, reshaping artistic materials and possibilities. Photography emerged as a new medium, fundamentally changing how humans captured reality. Artists were now influenced by mechanical reproduction and began exploring new styles such as Impressionism, which focused on light and perception.
The 20th Century: Modernism, Technology, and New Media
Modern Art and Abstraction
The early 20th century was characterized by radical experimentation. Artists rejected traditional representation, embracing Cubism, Surrealism, and Abstract Expressionism. Technological innovations in materials and media enabled these artistic leaps.
Film, Animation, and Electronic Media
Cinema and animation transformed storytelling. With the first motion pictures in the late 1800s and animated films in the early 1900s, visual art expanded into moving images. Electronic media continued to mature, adding sound and color, and later digital editing tools.
Digital Revolution: Computers and Creative Software
Entering the Digital Age
The advent of computers brought a seismic shift in creative processes. Artists could now leverage digital tools such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and 3D modeling software. These tools expanded the definition of art from physical material to virtual creation.
Digital Painting and Illustration
Digital painting tools allow artists to mimic traditional media or invent entirely new visual styles. Techniques like layering, brushes with dynamic effects, and real-time editing accelerated creative workflows, enabling experimentation without material waste.
3D Modeling and Virtual Sculpting
Beyond flat images, digital tools such as Blender, ZBrush, and Maya introduced digital sculpture and 3D modeling. These tools are now essential in film, gaming, architecture, and product design.
Interactive and Immersive Technologies
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR have opened immersive realms for artists and audiences. VR can place viewers inside fully realized environments, while AR can overlay art onto real physical spaces. Museums and digital installations increasingly use these technologies to enhance engagement.
Interactive Installations and Sensors
Artists are now incorporating motion sensors, sound triggers, and audience interactivity into installations. These works react in real time to human presence, creating dynamic, participatory art.
AI and Machine Learning in Art
AI-Generated Art
Artificial Intelligence has become a powerful creative partner. Machine learning algorithms such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) can generate images, reinterpret styles, or create entirely new visual forms. Tools like DALL-E and Midjourney are widely adopted by both hobbyists and professionals.
Ethical and Philosophical Questions
The rise of AI art has triggered debates around authorship, originality, and the role of algorithmic bias. Questions include: Who owns AI-generated artwork? Is AI creativity real creativity?
Art in the Blockchain Era
NFTs and Digital Ownership
Blockchain technology introduced NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), enabling verifiable ownership of digital art. This innovation has reshaped how digital art is bought, sold, and collected — even allowing artists to receive royalties on secondary sales.
Market Impacts and Criticisms
While NFTs have generated significant revenue, questions persist about environmental impact (due to energy use), speculative pricing, and accessibility for emerging artists.
Contemporary Practices: Hybrid and Cross-Disciplinary Art
Collaboration Between Art and Science
Contemporary creators often collaborate with engineers, scientists, and data analysts. Projects now explore data visualization, bio art, and environmental sensors, merging scientific inquiry with aesthetic expression.
Performance and Tech-Enhanced Live Art
Live performances now integrate projection mapping, motion tracking, and AI visuals. Technology amplifies theatrical and musical expression, igniting new forms of interactivity.
Future Frontiers: What’s Next in Art and Technology?
Quantum Computing and Generative Systems
Quantum computing offers potential for new generative art systems that explore complexity beyond classical computation. While still emerging, these technologies could redefine creative computation.
Global Digital Access and Cultural Exchange
As technology becomes more accessible globally, diverse artistic perspectives gain international platforms. This democratization enables non-Western art forms to influence mainstream digital culture.
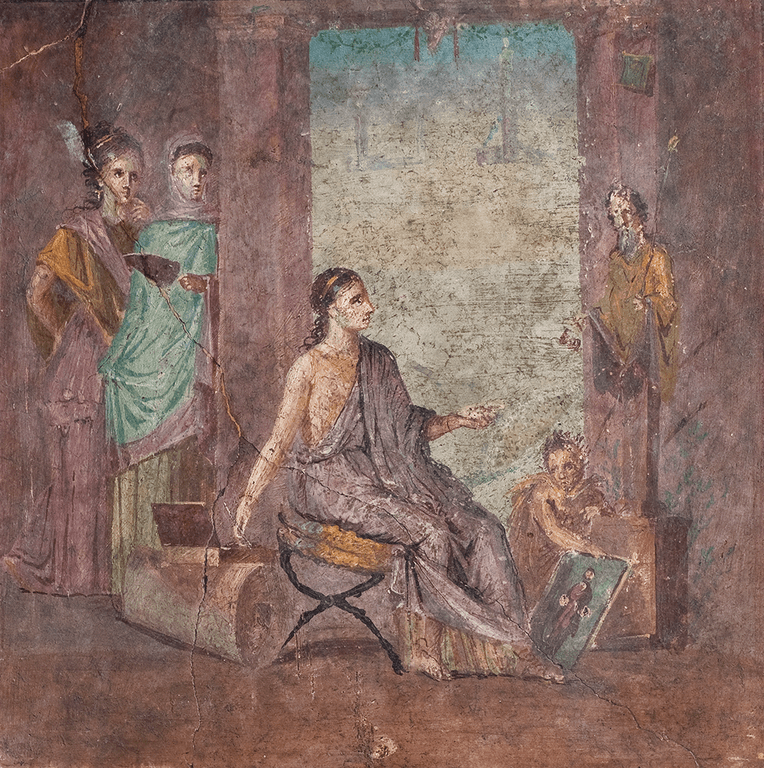




Conclusion
From the earliest pigments applied to stone walls to breathtaking digital environments rendered by code, the evolution of art reflects humanity’s persistent drive to innovate. Technology has not supplanted the human impulse to create — it has amplified it. As tools continue to evolve, so too will the ways artists conceive, produce, and share their visions.